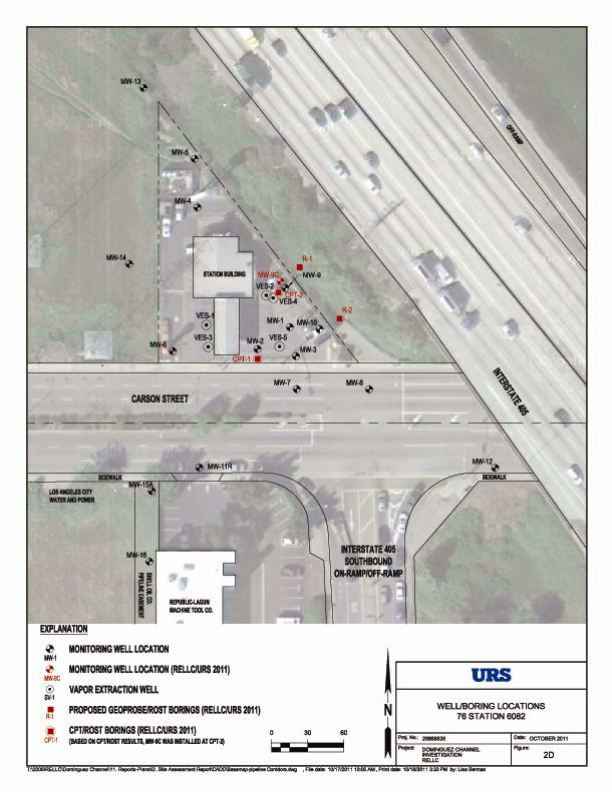
– Advanced four soil borings to test for soil type and petroleum impacts using Cone Penetrometer Test
(CPT) and/or Rapid Optical Screening Tool™ (ROST™) technologies (these technologies help identify
petroleum impacts at various depths)
– Installed and sampled one onsite groundwater monitoring well
– Chemically analyzed soil samples collected during the well installation
– Chemically analyzed groundwater samples collected from onsite and offsite groundwater monitoring
wells
Summary of Results: Test results of soil, groundwater, and residual petroleum samples collected at the 76 Station revealed the presence of the common gasoline additive methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE), which was not detected in similar types of samples collected from where petroleum sheen was observed on the channel. Furthermore, a number of monitoring wells were installed between the 76 Station and the area where petroleum sheen was detected on the channel, which showed no indication of petroleum on the groundwater. On the basis of these results, gasoline impacts at the 76 Station are not associated with the petroleum sheen detected in the channel. This site has an active remediation system for the 76 Station gasoline release, which will continue to operate until appropriate regulatory approved cleanup levels are reached.
In February 2012, the Los Angeles Regional Water Quality Control Board (LARWQCB) agreed that the 76 Station is not likely a contributor to the petroleum hydrocarbon release in the channel and determined
that no further action associated with the Dominguez Channel release was necessary at the 76 Station.